Are you still doing daily meetings in the format suggested by Scrum? The three famous questions:
- What did you do yesterday?
- What are you going to do today?
- Are there any obstacles?
Do yourself a favor and stop.
It might have been a useful practice two decades ago. But it is not anymore. Not in that form.
The Old Cure
Here’s the thing. The ideas behind Scrum date as far back as the 80s, and its first applications happened in the 90s. Yes, it’s that old. But that itself doesn’t deserve criticism.
However, when you look at the 2000s, when Scrum got its prominence, your average team’s tooling looked very different. The visual boards were yet to become popular. The state-of-the-art task management system was a filtered list.
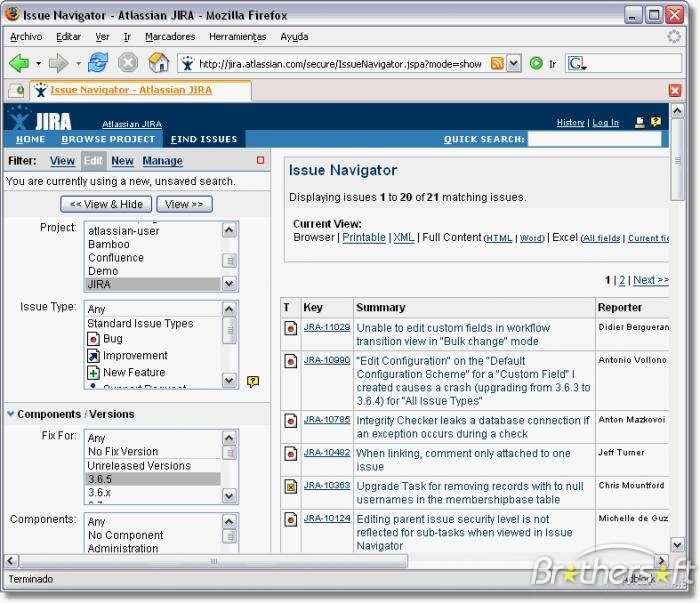
No one in the IT industry seriously talked about limiting WIP then, so we were drowned in an excessive amount of ongoing tasks. That made navigating long, long lists of work items even more of a maze from nightmares.
It’s no wonder that people saying what they were doing yesterday and what they plan to do today was a refresher.
The New Situation
Fast forward 10 years, and teams suddenly have very readable visual boards as a standard practice. Limiting work in progress may still be a challenge, but we’ve gotten progressively better.
Also, new visualization standards allow for better comprehension of whatever is in flight. Even Jira caught up.
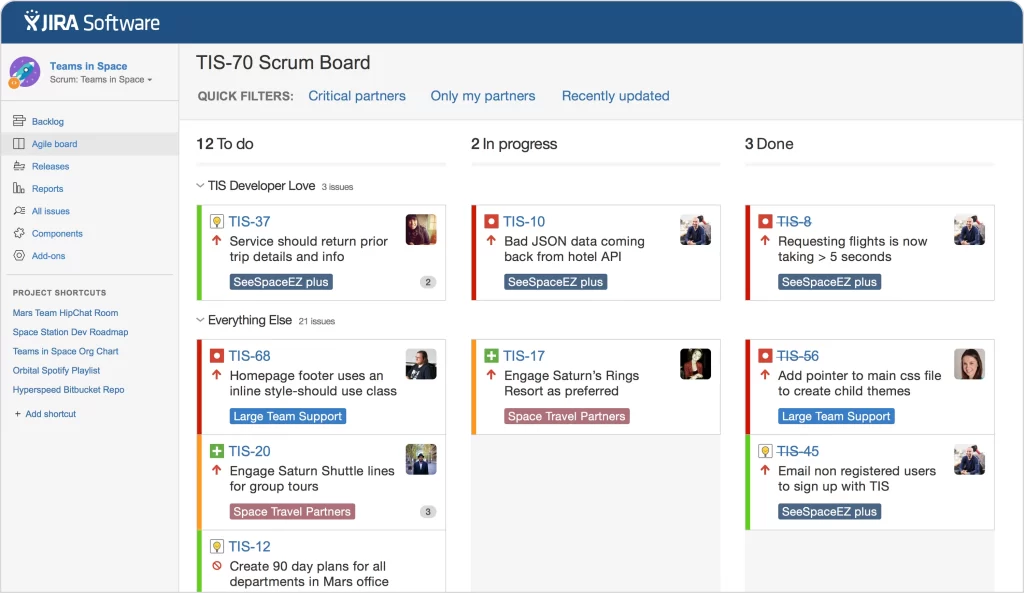
As long as:
- the board is up to date
- there’s even remotely reasonable amount of work in progress
we can clearly see who’s doing what.
How? Just look at the board—it’s all there; thank you very much.
And if, by any chance, the board would suggest that a person still works on 5 different things, then it’s not the form of the daily meetings that is the main problem.
Who Cares?
If you still think the old form of the daily updates makes any sense, look at people’s engagement during them. There’s precisely one person who’s interested in the entirety of the updates.
The Scrum Master.
For the rest of the team, it’s a ritual they follow out of habit. At best, they are interested in what a couple of people working on the most related tasks are doing, and then they’re off again.
So it’s like a theater with many actors and just one attendee (the Scrum Master).
It’s even worse. Almost all that information is readily available on the visual board. So that one person could have gotten it without getting everyone involved.
Not Just a Status Update
That’s the point where people tell me that I describe a daily meeting as a glorified status update, which it wasn’t meant to be.
Fair enough. So what is it?
A way for a remote team to get together and gel? Fine, get together and gel. I doubt that answering who does what is the best way to do it.
So, maybe, it’s a place where we discuss obstacles and problems. Fantastic! That’s actually the only original question that is still useful. Then, ask only that bloody question and be done with it.
Whatever the purpose of the meeting is, name it. I bet there’s a better format to address that very purpose.
And yet, in 2025, people will still answer those three questions invented three decades ago.
Daily Around the Board
The intention behind the original standup format was a team sync-up. That goal is still worth pursuing. However, we have options that weren’t available a quarter of a century ago.
My default way of running dailies relies on four elements:
- We use blockers extensively to show any impediments
- We keep the visual board up to date (it’s “the single source of truth”)
- We run dailies around the board
- We read the board from right to left (or from most to least done) and focus purely on blockers
That’s it. It’s enough to focus on the important stuff. The rest is business as usual and not worth mentioning.
You can easily cut the daily meeting time by half (or more), make it more engaging, and (a bonus) use it as an encouragement to keep the board up to date.
There’s literally no coming back.
The Purpose
Sadly, we still stick to practices. They might have been visionary decades back, but somehow, we stopped asking about their purpose and blindly stuck to them.
If we did, we would challenge many of the techniques we use.
Ask yourself this question: If Agile were invented today, what practices would it devise? It would most definitely be different from what you’d find in a Scrum Guide.
So do yourself a favor, stop answering the three standup questions, and, for a change, start using this daily hangout to make something useful.
That’s what Agile intended us to do, after all.